Have you ever wondered how the technicians manage to organize the fiber optic cables in huge networks? With dozens—or even hundreds—of tiny fibers within a single cable, identification accuracy is critical. So, here the role of the color codes of fiber optic cables comes into play! These uniform color schemes aid in proper installation, avoiding expensive errors, and simplifying troubleshooting.
Thus, in this guide, you will understand the reasoning behind the color coding of fiber optic cables, its importance of it, and the role of TIA-598C in efficient network management. So, let’s delve into this fascinating breakdown of fiber coloring scheme!
Figure no 1 Fiber Color Code Guide
1) Understanding Optical Fiber Color Code
You know fiber color coding is a technique that ensures clear identification for each fiber strand and guarantees proper mechanization. This technique observes TIA-598C standards that dictate how markers and buffer tubes are organized into strands. Without this standard, fiber networks would just be struggling to reconnect cables, thus enduring expensive repair cycles, and losing time.
Figure no 2 Color Code For Fiber
Importance of Color Coding System
We all know that Optical fibers carry precise information whether it is high-speed internet, telephonic services, or television broadcasting. Giant optical cables can bundle hundreds of fibers and each may serve the purpose of receiving or relaying data. In case these fibers and their connections are wrongly identified, your network is bound to slow down, get interrupted frequently or even collapse completely. So, it is crucial to adhere to standards based on color coding. This allows us to quickly find matches and connect appropriately, thus guaranteeing speedy installations, simpler network tests, and more seamless services.
Buffer Tubes and Fiber Strands in Color Coding
In a fiber optic cable, a system is kept organized with the use of strands of buffer tubes and fibers. For instance;
- Buffer Tubes: These are protective sleeves that hold several to a lot of fiber strands. They protect fiber strands from bending or moisture. Moreover, in high fiber counted cables, these tubes are arranged in a certain order to enable easy tracking, maintenance, and expansion of networks.
- Fiber Strands: These are the microscopic glass fibers enclosed within buffer tubes that are capable of passing through light signals. Each fiber uses a certain slot as well as a predetermined set of colors. This guarantees that at both ends of the cable, connections will be made to precise and matching counterparts, thus protecting data from loss or interference.
Moreover, a person on Qoura named Nagaraj T M who is the CEO at Unisol Communications Pvt Ltd., has also shared his reviews about fiber color code. According to him, we get valuable information from the fiber color code like their core diameter and type of communication network. For instance, the yellow color indicates a Single mode fiber with a core diameter of about 8-10 microns.
2) Color Coding Guide for Multi-Core Fiber Optic Cables
i) 2-Core Fiber Optic Cable Color Code
A 2-core fiber optic cable has two glass fibers inside. One fiber sends data, one receives it. The connecting wires are color-coded blue and orange, which helps in their proper connection.
- Color Code Breakdown
| Fiber 1 | Fiber 2 | |
| 2-core fiber optic | Blue (Tx – Transmit) | Orange (Rx – Receive) |
- Common Uses
These cables are widely used for providing high-speed and stable internet connections at home. Moreover, It is also used in CCTV camera installations so that clear video transmission can be achieved over large distances. Pus, you can find them in some medical equipment where data has to be transmitted with speed and precision for real-time monitoring and diagnostics. Apart from this, they are also very cheap and easily installed, making them a good choice for short-distance communication.
ii) 4-Core Fiber Optic Cable Color Code
In a 4-core fiber optic cable, there are four glass fibers with each transmitting light signals: The first two fibers handle the main data flow, while the extra two provide backup or additional bandwidth.
- Color Code Breakdown
| Fiber 1 | Fiber 2 | Fiber 3 | Fiber 4 | |
| 4-core fiber optic | Blue (Tx – Transmit) | Orange (Rx – Receive) | Green (Extra data channel) | Brown (Extra data channel) |
- Common Uses
4-core fiber cables are extensively used in small office networks, helping to connect multiple devices including routers, switches, and computers. They are also found in security systems, ensuring stable video feeds from surveillance cameras. Moreover, in smart homes, 4 core fiber cables support high-speed automation systems, enabling better internet for smart TVs and voice assistants. Their reliability makes them a great option for residential as well as small-business networking.
iii) 6-Core Fiber Optic Cable Color Code
A 6-core fiber optic cable consists of six fibers with each allowing multiple streams of data concurrently. The first 4 are dedicated to main network traffic, while the last two provide redundant pathways to ensure continuity of service.
- Color Code Breakdown
| Fiber 1 | Fiber 2 | Fiber 3 | Fiber 4 | Fiber 5 | Fiber 6 | |
| 6-core fiber optic | Blue (Tx – Transmit) | Orange (Rx – Receive) | Green (Extra data channel) | Brown (Extra data channel) | Slate (Backup line) | White (Backup line) |
- Common Uses
These cables have a critical role in an organization’s end-to-end network infrastructure as they facilitate the transfer of data at a very high speed within office buildings and other commercial structures. Moreover, in traffic management systems where real-time updating of changeable signals is paramount, they are equally important. Similarly, in industrial automation, 6-core cables allow communication between machines and sensors to take place. Thus, their capabilities in supporting multiple connections enable greater versatility and dependability in networking.
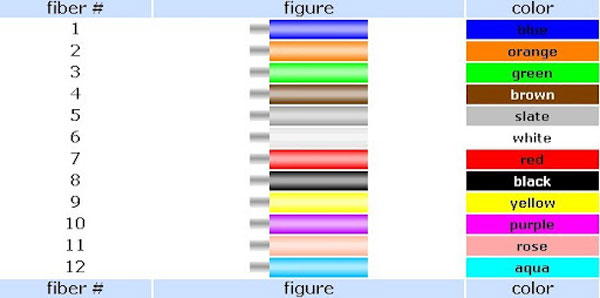
Figure no 3 1-12 Core fiber Color Chart
iv) 8-Core Fiber Optic Cable Color Code
8-core fiver optic cables are specially designed for medium-sized networks. This is because they are equipped with additional fibers which increases its bandwidth capacity allowing for a higher rate of data transfer as well as increasing its potential for future growth. The designated colors of the coded fibers enable easier identification during installation and system maintenance.
- Color Code Breakdown
| Fiber 1 | Fiber 2 | Fiber 3 | Fiber 4 | Fiber 5 | Fiber 6 | Fiber 7 | Fiber 8 | |
| 6-core fiber optic | Blue (Tx ) | Orange (Rx) | Green | Brown | Slate | White | Red | Black |
- Common Uses
The 8-core fiber optic cables are used in the campus network to link between several buildings to provide high-speed internet access. They are also used in relaying services that require audio and video signal transmission without any delays. Plus, these cables also offer high reliability and security for data transmission between different locations during military and defence activities.
v) 12-Core Fiber Optic Cable Color Code
Designed for multi-stream connections and data transfer, a 12-core fiber optic cable supports high-speed networking. The additional fibers enable load balancing, which means data can be switched to different paths to reduce congestion.
- Color Code Breakdown
| Fiber 1 | Fiber 2 | Fiber 3 | Fiber 4 | Fiber 5 | Fiber 6 | Fiber 7 | Fiber 8 | Fiber 9 | Fiber 10 | Fiber 11 | Fiber 12 | |
| 6-core fiber optic | Blue (Tx ) | Orange (Rx) | Green | Brown | Slate | White | Red | Black | Yellow | Violet | Rose | Aqua |
- Common Uses
These cables are utilized in modern-scale data centres that require processing massive amounts of data within seconds. They are also implemented in the communication systems of the railway for proper coordination between the stations and the trains. In the medical field, 12-core fiber cables help transmit high-resolution scans in real time to improve diagnostics during procedures.
vi) 24-Core Fiber Optic Cable Color Code
A single 24-core fiber optic cable possesses two sets of twelve fibers which supports colossal amounts of data transfer. The additional fibers provide redundancy, scalability, and enhanced network efficiency.
- Color Code Breakdown
| Fiber 1-12 | Fiber 13-24 | |
| 24-core fiber optic | Same as above ( Blue, orange, green, brown, slate, white, etc.) | Same as 1-12 but with different markings |
- Common Uses
These cables guarantee uninterrupted internet service to dozens of users, which makes them indispensable in telecommunication networks. In a hospital, these cables are used for quick transfer of large medical files such as X-ray pictures and patient records. In metro networks, 24-core fiber cables ensure reliable and rapid connection for smart-city applications.
Figure no 4 24-core fiber Color Chart
vii) The 48-core Fiber Optic Cable Color Code
Like all cables, a 48-core cable is constructed to allow super speedy data transmission. Parallel channels and cables increase reliability. The high number of fibers also increases efficiency by eliminating bottlenecks.
- Color Code Breakdown
| Fiber 1-12 | Fiber 13-24 | Fiber 25-36 | Fiber 37-48 | |
| 48-core fiber optic | Same as above ( Blue, orange, green, brown, slate, white, etc.) | Repeat with black strip marking | Repeat with double-ring marking | Repeat with dashed makings |
- Common Uses
These cables serve hyperscale data centres, enabling millions of online transactions a day. Moreover, in cloud computing where data is stored and accessed globally, the cables are vital. Similarly, in smart city infrastructure, 48-core fiber cables connect IoT devices, public services, and surveillance systems providing real-time data.
3) Connector Color codes
In past, Multimode fiber connectors were grey, orange, or black while single-mode connectors were colored yellow. Now with the introduction of metallic connectors, different colors are used to identify specific types of fibers. These colors allow quick recognition and matching of connectors by technicians which guarantees the correct fiber connections.
Moreover, Strain relief and mating adaptors are also coded with the same color for consistency and ease of use during fiber optic installations.
Figure no 5 Fiber Connector Color Code
| Fiber Type | 62.5/125 Multimode | 50/125 Multimode | 50/125 Multimode | OM5 (Wideband MM) | Single-Mode | Single-Mode APC |
| Connector color | Beige | Black | Aqua | Lime | Blue | Green |
4) Fiber Optic Cable Jacket Color
| Fiber Type | 62.5/125 Multimode | 50/125 Multimode | 50/125 Multimode | OM5 (Wideband MM) | Single-Mode (os1, os2) | Single-Mode APC | Polarization-Maintaining (PM) Single-Mode |
| Jacket Color | Orange | Orange | Aqua | Lime | Yellow | Green | Blue |
5) Key Takeaways
All in all, for optimal network performance, it is vital that color coding is accurate. That is why a TIA-598C standard for color coding is recommended. This also helps reduce misconnections, and downtime and simplifies troubleshooting. So, if you are looking for reliable industry-compliant fiber optic cables then you can trust DEKAM Fibers. We are China’s best custom fiber optic cable supplier and manufacturer. So, the right selection increases the chances of having a fast and stable network. Don’t waste time, and contact DEKAM to solve your networking problems!