FTTx (Fiber to the X) is the backbone of ultra-fast internet, but where the fibre stops makes all the difference! It determines how exactly fibre optic internet gets to you, whether that is to your home, building, desk or else curbside. Well! Fibre employs light signals which guarantee speed, unmatched reliability, and a performance that’s unparalleled. But not all fibre connections are of the same standard!
That’s why in this guide, we’ll provide a detailed discussion on what the FTTX technology is and also discuss in detail its various forms like FTTH, FTTA, FTTB, FTTC, FTTD, FTTE, FTTN, FTTO, FTTP, FTTR. So, keep reading!
Figure no 1 FTTX technology
1) Understanding FTTX technology
FTTx (Fiber to the X ) where X means where the fibre optic cables are located. Moreover, compared to DSL that utilizes copper wires to transmit data they have much higher speeds and lower latency.
If you use traditional broadband like DSL, your maximum speed might be around 100 Mbps (megabits per second). However, with fibre optic connections you will be able to receive 10 Gbps (gigabits per second) or more; that’s 100 times faster! Furthermore, you receive better bandwidth which means that multiple devices streaming on the internet at the same time won’t lead to your internet slowing down.
Depending on how close the fiber gets to you FTTH (Fiber to the Home), FTTB (Fiber to the Building), FTTC (Fiber to the Curb), and FTTN (Fiber to the Node) are different types of FTTx. However, keep in mind that if you have full-fibre access, your internet experience will be drastically improved in regard to speed, latency, and access performance.
2) Exploring FTTX variations: FTTH vs FTTA vs FTTB vs FTTC vs FTTD vs FTTE vs FTTN vs FTTO vs FTTP vs FTTR
| Overview | Best For | Limitations | |
| FTTH | Fiber runs straight to your house for the fastest speeds with no interference | Homes needing top speeds (gaming, streaming, remote work) | Expensive, limited availability. |
| FTTA | Fibre reaches an apartment building, is shared among residents | Apartment residents need a fast internet | Shared bandwidth may slow speeds |
| FTTB | Fibre is brought to the building, then copper or Ethernet is used within the building. | Offices & apartments want better speeds compared to DSL | Internal wiring affects performance. |
| FTTC | Fiber runs to a street cabinet and data is carried via copper to the homes. | Budget users need better speeds than DSL. | The further from the cabinet you are, the lower the speed. |
| FTTD | A desk is connected directly to fiber ensuring maximum performance. | Businesses and professionals seeking ultra-fast internet. | Rare outside of large enterprises and expensive. |
| FTTE | High-speed reliable internet access is provided at large business locations via fibre. | Enterprises and corporate offices. | Not for home users, costly |
| FTTN | Fiber stops at a neighbourhood node and data is carried copper to the home | Casual browsing and budget users. | The further from the node you are, the lower the speed. |
| FTTO | Fiber is plugged directly into the offices for stable, high-speed access | Business and IT firms with a need for consistency in speed | No residential use, high cost. |
| FTTP | Fiber Internet access is provided throughout the building. | Reliable and resistant to the test of time. Long-lasting concern for high-speed internet users | Costly to install. |
| FTTR | The fibre line goes straight to the router, providing unparalleled speeds at home. | Offers a lag-free connection to high-volume internet consumers. | Not widely available. |
i) Fiber to the Home (FTTH)
FTTH is a broadband access option in which a fibre optic cable is run directly to the user’s home, so internet service is provided with the lowest signal attenuation. With FTTH, there are no speed drops due to distance, unlike DSL or cable. FTTH ensures high speeds are maintained throughout the distance which guarantees a positive user experience.
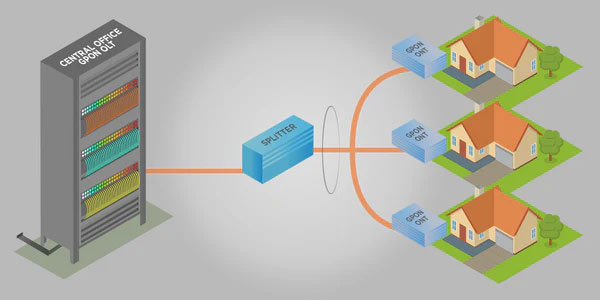
Figure no 2 FTTH ( Fibre to the Home )
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + Blazing-fast speeds up to 10 Gbps (100× faster than DSL).+ Ultra-low latency for smooth gaming, streaming, and calls. + Stable, long-distance connection with no signal loss. + Supports multiple devices with no slowdowns. + Future-proof technology—no need for frequent upgrades. | – Higher setup cost. – Fiber must be available in your area. – Limited availability in some locations. – Longer installation time. |
- Use Cases
FTTH is ideal for users who require ultra-high-speed connectivity from home. For instance;
- To stream video content at 4k or 8k resolution you can expect zero delays while playing online games.
- If you work remotely and attend virtual video meetings.
- If you want smart homes and have multiple devices that run simultaneously.
ii) Fiber to the Apartment (FTTA)
With FTTA, broadband services are extended to apartment blocks via fibre optic cables. However, the final connection to the unit utilizes Ethernet or coaxial cables, which effectively provide high-speed internet access. But you will face a possible decrease in speed due to the building’s wiring.
Figure no 3 FTTA Solution
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + High-speed fibre shared across the building. + More affordable than FTTH + Quick and easy installation compared to FTTH. | – Speeds may drop if too many users are online. – Shared connections may cause congestion at peak times. |
- Use Cases
FTTA comes in handy if you live in an apartment building and want access to faster internet speeds without having to wait for an installation of fibre. For instance, it works well for:
- HD and 4K movie streaming.
- Online gaming.
- Remote work that relies on video calls.
iii) Fiber to The Building (FTTB)
FTTB brings fibre optics to the building with the last leg of the connection to the unit using Ethernet, coaxial or even legacy copper wiring.
Figure no 4 FTTH vs FTTB
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + Speeds up to 500 Mbps, faster than DSL. + Faster than FTTC and FTTN. + More affordable than FTTH. | – Speed drops if you’re far from the cabinet. – May need upgrades in the future. – Still uses old cables, so it’s not fully fiber. |
- Use Cases
If you reside in a multi-tenant building and desire to have fast internet, FTTB is suitable for you. This includes:
- Home offices that require dependable internet for video calls.
- Small business owners who require dependable internet services.
- Residents of apartments who wish to have reliable internet for streaming and gaming.
iv) Fiber to the curb (FTTC)
FTTC implies that fibre optic cables are available to a street cabinet near your home. But the connection to your house is done over copper or coaxial cables.
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + Brings fibre closer to homes than FTTN. + Cheaper than FTTH and FTTB. + Faster than DSL and cable. | – Uses copper for the final stretch, reducing speed. – Speed decreases with distance from the curb cabinet. – Requires maintenance of older copper lines. |
- Use cases
If higher speeds than DSL or cable are required in your area, FTTC might be the right option for you. It’s designed for:
- Basic or casual streaming and internet browsing.
- Families that multi-device at the same time.
- Basic remote work with the occasional video call.
v) FTTD (Fiber to the Desk)
FTTD refers to the direct installation of fibre strands to one’s desk or office, granting the user the most stable and highest-speed connection.
Figure no 5 FTTD solution
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + Direct fibre to your desk, ensuring max speed and reliability. + Zero interference and ultra-low latency. + Ideal for professionals needing top performance. | – Expensive – Not common for home users. – Requires specialized installation. |
- Use Cases
It’s great for:
- Hardcore gamers who need ultra-low latency.
- Business offices that demand stable, high-speed internet.
- Data file tech specialists.
vi) FTTE (Fiber to the Enterprise)
FTTE connects businesses to the internet via fibre optics, guaranteeing internet connectivity for large corporations.
Figure no 6 FTTE Solution
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + Delivers dedicated fiber to business locations. + Ensures stable and high-speed connectivity. + Supports large-scale business operations. | – Costly compared to FTTB or FTTN. – Not needed for smaller businesses. – Requires professional setup and maintenance. |
- Use Cases
If your business relies on high-speed and seamless internet connectivity, FTTE is for you. Ideal candidates include:
- Corporate headquarters of companies with a mid-range to high employee count.
- Banks shifting large volumes of sensitive data over the internet requires secure high-speed transactions.
- Cloud computing and big data services from Tech Companies.
vii) FTTN (Fiber to the Node)
FTTN delivers fibre optic cable to a local node, and DSL or coaxial cables provide the last-mile connection to the house.
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + More widely available than FTTH. + Cheaper and faster to install than full fiber. + Better than traditional broadband options. | – Slower than FTTB, FTTD, or FTTH. – Speed drops as the distance from the node increases. – Still relies on copper for final delivery. |
- Use Cases
FTTN is good for you if full fibre isn’t available, but you want something faster than DSL. It’s best for:
- Participants casually browse and stream.
- Budget users looking for something reliable.
viii) FTTO (Fiber to the Office)
FTTO is a business-focused fibre connection that offers high-speed, dedicated internet to company offices.
Figure no 7 FTTO Solution
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + Ensures high-speed, stable internet for offices. + More reliable than cable or DSL. + Supports cloud computing and remote work. | – Expensive compared to FTTN or FTTB. – Not suitable for home users. – Requires professional installation. |
- Use cases
FTTO is great for businesses that need a stable and fast connection. It’s best for:
- Secure-law data firms.
- Cloud-servicing IT companies.
ix) FTTP (Fiber To The Premises) & FTTR (Fiber To The Router)
Both methods bring fibre to your home and business, providing the fastest and most reliable internet.
Figure no 8 FTTC vs FTTN vs FTTP
- Advantages & Disadvantages
| Pros | Cons |
| + No slowdowns with full fibre. + Optimal for future internet speeds. | – Installation costs are high – Limited availability |
- Use Cases
Home and business users who strive for the fastest internet speeds will benefit most from FTTP & FTTR.
3) Final Words
In short, I must say that making the right choice in an FTTx connection can change your speeds and reliability for the internet in the most positive way. No matter if it is to your home, building, curb, or desk, there are advantages to each type. However, besides all FTTH is the most reliable, while the hybrids balance cost and coverage.
Knowing this allows you to make the most informed decisions for internet speed, performance, and longevity. So, if you want customized FTTH solutions, then visit our website today. We have 12 production lines and over 52 production machines, thus providing highly reliable products. Request an instant quote today!