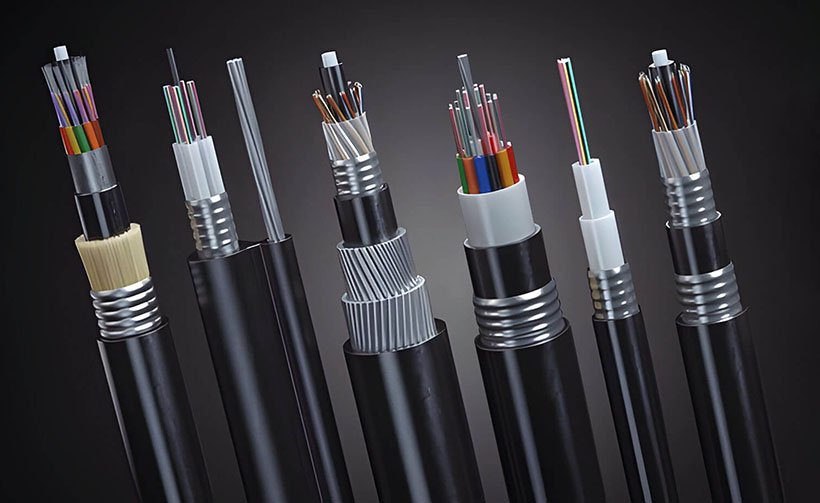
Outdoor fiber optic cable forms the rugged backbone of modern telecommunications, carrying high-speed data across cities, rural regions, industrial sites, and even under oceans. Designed to survive decades of UV exposure, temperature swings, moisture, mechanical stress, and rodent attacks, these cables are essential for FTTH, 5G backhaul, long-haul trunks, and enterprise connectivity.
As of January 2026, global fiber deployments exceed 1.6 billion fiber-kilometers annually, with FTTH connections nearing 2.5 billion. Choosing the right كابل الألياف الضوئية الخارجي directly affects network uptime, maintenance costs, and scalability. A poor choice can lead to water ingress, attenuation spikes, or cable breaks, costing operators millions.
This guide covers everything: definitions, construction, all major types, specifications, selection framework, recommended models, installation procedures, maintenance, cost analysis, case studies, pitfalls, and 2026–2030 trends.
What Defines an Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable?
Outdoor fiber optic cable is optical cable engineered for unprotected external environments, distinguishing it from indoor cable through enhanced protection.
Key Differences from Indoor Fiber Optic Cable
| ميزة | كابل الألياف الضوئية الخارجي | كابل الألياف الضوئية الداخلي |
|---|---|---|
| Sheath | Thick UV-stabilized PE/MDPE/HDPE | Thin PVC/LSZH/OFNP |
| Water-blocking | Gel-filled tubes + swellable yarns/tapes | Minimal or none |
| Armor | Steel tape, aluminum, FRP rods | None or light aramid |
| Strength members | High-tensile aramid or steel (2700–20000 N) | Low-tensile aramid (100–500 N) |
| Temperature range | –40°C to +85°C operating | –20°C to +70°C |
| UV resistance | 25–50 years | Limited |
| Standards | IEC 60794, Telcordia GR-20 | UL OFNP, IEC 60332 |
Indoor fiber optic cable used outdoors fails quickly: UV cracks sheathing, moisture causes hydrogen loss, mechanical stress breaks fibers.

Why Selection Matters in 2026
- 5G densification needs aerial cables for small cells.
- Rural broadband requires long-span designs.
- Climate change increases extreme weather.
- Sustainability pushes for longer lifespan and recyclable materials.
Poor choices cause >$2.5 billion in annual global repair costs.
Types of Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
Loose-Tube Stranded Cable
Fibers float in gel-filled or dry-block PBT tubes.
Sub-types:
- Direct-buried: Double sheath + corrugated steel tape armor. Used for underground without conduit. Crush resistance 3000 N/100 mm.
- Duct: Single sheath, low-friction outer layer. Designed for pulling into conduits.
- Aerial lashed: Aramid-reinforced for attaching to existing messenger wire.
Capacities: 12–864 fibers. Applications: feeders, metro rings.
Figure-8 Self-Supporting Cable
Integrated messenger wire (steel or FRP) forms “8” cross-section.
Sub-types:
- Steel messenger: 3000–8000 N tensile, spans 300 m.
- All-dielectric FRP: lightning-safe, lighter weight.
- Micro figure-8: 5–8 mm diameter for urban poles.
Applications: pole-to-pole, rural FTTH. Advantages: no separate lashing needed.

ADSS (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting)
No conductive metal; uses aramid yarns and FRP rods.
Sub-types:
- Standard ADSS: 24–144 fibers, spans 800 m.
- High-tensile ADSS: reinforced aramid, spans 1000–1500 m.
Applications: co-deployment with high-voltage power lines.
كابل الألياف الضوئية المدرع
Adds corrugated steel tape or interlocking armor.
Sub-types:
- Single armor: moderate protection.
- Double armor: extreme crush/rodent resistance.
Applications: direct burial, industrial sites.

Submarine and Underwater Cable
Multi-layer steel wire armor, hydrogen-absorbent jelly, optional copper conductors.
Applications: river, lake, ocean crossings.
Ribbon Cable
12–24 fiber ribbons in tubes, enables mass fusion splicing.
Capacities: 864–1728 fibers.
Applications: high-capacity trunks.
Micro-Cable and Blown Cable
4–10 mm diameter, low-friction sheath.
Applications: blown into microducts in urban areas.
Hybrid Cable
Combines optical fibers with copper power conductors or sensing fibers.
Applications: remote 5G sites, smart grid.
Key Specifications for Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
Optical Performance
- Attenuation: single-mode ≤0.35 dB/km @1310 nm, ≤0.22 dB/km @1550 nm
- Polarization mode dispersion (PMD): ≤0.1 ps/√km
- Multimode bandwidth: OM4 >4700 MHz·km @850 nm
Mechanical Performance
- Tensile strength: 2700–20000 N (short/long term)
- Crush resistance: 2000–5000 N/100 mm
- Impact resistance: 10–25 J
- Bend radius: 10–20× cable diameter
Environmental Performance
- Temperature: –40°C to +85°C operating
- Water penetration: no leakage (IEC 60794-1-22 F5B test)
- UV resistance: no cracking after 2000 hours exposure (ASTM G154)
- Chemical resistance: withstands pH 2–12, oils, fuels
أنواع الألياف
- Single-mode: G.652D (standard), G.657A2/B3 (bend-insensitive)
- متعدد الأوضاع: OM3 (10G), OM4 (40G/100G), OM5 (SWDM)
Selection Guide – Step-by-Step Framework
Step 1: Determine Installation Environment
- Aerial → figure-8 or ADSS
- Direct buried → armored loose-tube
- Duct → micro-cable
- Submarine → heavy armored
Step 2: Assess Environmental Threats
- Rodents → armored
- Ice/wind → high-tensile figure-8
- Lightning → all-dielectric
- Flood-prone → gel + swellable tape
Step 3: Define Capacity and Fiber Type
- Distribution (12–48 fibers): figure-8 drop
- Feeder/backbone (144+ fibers): loose-tube or ribbon
Step 4: Evaluate Performance Needs
- Long spans → low attenuation, high tensile
- Tight bends → G.657A2 fibers
Step 5: Calculate Total Cost of Ownership
- Initial price + installation + maintenance over 25 years
Step 6: Verify Compliance & Supplier Reliability
- Certifications (IEC, Telcordia)
- Manufacturer track record
Recommended Models for 2026 Applications
Aerial FTTH – Figure-8 Loose-Tube (GYTC8Y)
- Fibers: 12–144
- Messenger: galvanized steel
- Tensile: 5000 N
- Price: $0.065–0.40/m
- Span: 300 m
- Use: pole-to-home drops
Direct Buried Trunk – Double-Armored Loose-Tube (جي واي تي ايه 53)
- Fibers: 24–288
- Armor: corrugated steel + aluminum tape
- Crush: 4000 N/100 mm
- Price: $0.12–0.55/m
- Use: underground feeders

High-Voltage Co-Deployment – اي دي اس اس (All-Dielectric)
- Fibers: 24–144
- Strength: aramid + FRP
- Tensile: 10000 N
- Price: $0.12–0.75/m
- Span: 800 m
- Use: power line routes
Urban Micro-Duct – Blown Micro-Cable (GYFXTY)
- Fibers: 12–144
- Diameter: 5–8 mm
- Price: $0.12–0.45/m
- Use: blown into existing ducts
Hybrid 5G Small Cell – Fiber + Power Hybrid
- Fibers: 24 + 4 copper pairs
- Price: $0.12–0.32/m
- Use: remote radio units
Installation Best Practices
Aerial Installation (Figure-8 & ADSS)
- Survey poles and calculate sag/tension.
- Use payout stands with braking system.
- Attach suspension clamps every 150 m.
- Install vibration dampers in high-wind areas.
- Leave service loops at poles.
Direct-Buried Installation
- Dig trench 1–1.5 m deep. (How deep is fiber optic cable buried)
- Lay 10 cm sand bedding.
- Place cable with gentle curves.
- Cover with warning tape 30 cm above.
- Backfill with screened soil.
Duct Installation
- Clean duct before pulling.
- Apply lubricant.
- Monitor tension (never exceed rating).
- Use swivel connectors to prevent twist.
تركيب الغواصة
Specialized vessels, ROVs, burial plows.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
- Aerial: annual visual inspection + OTDR test
- Buried: biannual OTDR from access points
- Submarine: 5-year ROV surveys
Common Issues & Fixes
- Water ingress → locate with OTDR, reseal joints
- Rodent damage → install armor retrofit
- Attenuation rise → resplice affected section
- Excessive sag → re-tension or add supports
Predictive Maintenance
Use smart cables with embedded temperature/strain sensors.
Cost Analysis and Procurement Strategies
Typical 2026 Prices (per meter)
- Figure-8 aerial (12–48 fibers): $0.08–0.22/m
- Armored buried (48–288 fibers): $0.15–0.50/m
- ADSS (24–144 fibers): $0.15–0.45/m
- Submarine: $0.50–1.20/m
Total Cost of Ownership (25 years)
Aerial figure-8 often lowest TCO due to fast install and low maintenance.
Procurement Tips
- Buy direct from manufacturers for 25–40% savings.
- Request OTDR, tensile, crush, water-penetration reports.
- Prefer suppliers with overseas warehouses for faster delivery.
Innovations and Trends 2026–2030
- Smart cables with embedded sensors for real-time strain/temperature monitoring
- Ultra-high-density designs (864–1728 fibers) using ribbons
- Sustainable materials — recycled PE sheath, biodegradable fillers
- Hybrid cables combining fiber + power + sensing
- Self-healing outer layers using nano-coatings
Dekam Fiber is investing heavily in sensor-integrated and recycled-material cables.
Real-World Case Studies
Rural FTTH – Midwest USA
500 km figure-8 cable deployed in 2022. Installation cost 40% lower than lashed alternative. No failures after 2 years despite ice storms.
Urban 5G – Singapore
Micro-duct blown cable in existing conduits. Deployment completed in 2 weeks. 99.999% uptime.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
Outdoor fiber optic cable is mission-critical infrastructure. Select based on environment, mechanical needs, fiber type, and long-term TCO.
Dekam Fiber offers a full range of solutions — from figure-8 aerial to armored buried and smart hybrid cables — all with rigorous testing and 25-year warranties.
Contact Dekam Fiber for samples, engineering support, or competitive pricing.
The future of connectivity runs through reliable outdoor cable. Choose wisely.